1、删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点(中等)
自己的想法
方法一:快慢指针
- 执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
- 内存消耗:36.5 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了41.51%的用户
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
// 快慢指针
ListNode end = head, start = head;
// 移动快指针
while (n-- != 0) {
end = end.next;
}
if (end == null) {
return start.next;
}
// 向后移动
while (end.next != null) {
end = end.next;
start = start.next;
}
start.next = start.next.next;
return head;
}
}
看题解后
方法二:栈
- 执行用时:1 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了18.83%的用户
- 内存消耗:36.6 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了18.64%的用户
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
// 创建节点指向头节点,为了方便删除 head
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
Deque<ListNode> stack = new LinkedList<ListNode>();
ListNode cur = dummy;
// 入栈
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
// 出栈
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
stack.pop();
}
ListNode prev = stack.peek();
prev.next = prev.next.next;
ListNode ans = dummy.next;
return ans;
}
}
2、合并两个有序链表(简单)
自己的想法
方法一:迭代
- 执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
- 内存消耗:38 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了31.46%的用户
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode read = new ListNode();
ListNode node = read;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
node.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
node.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
node = node.next;
}
node.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
return read.next;
}
}
看题解后
方法二:递归
- 执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
- 内存消耗:38.1 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了12.66%的用户
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) {
return l2;
}
if (l2 == null) {
return l1;
}
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
// mergeTwoLists 返回的是 l1.next 和 l2 最小的头节点
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
}
3、环形链表(简单)
自己的想法
方法一:快慢指针
- 执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
- 内存消耗:39.6 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了35.62%的用户
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
// 快慢指针
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
try {
do {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next.next;
} while (fast != slow);
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
看题解后
不捕获异常
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
do {
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return false;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
} while (slow != fast);
return true;
}
}
方法二:Hash
- 执行用时:5 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了15.29%的用户
- 内存消耗:38.8 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了72.50%的用户
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<ListNode>();
while (head != null) {
if (!set.add(head)) {
return true;
}
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}
}
4、环形链表 II(中等)
看题解后
方法一:快慢指针
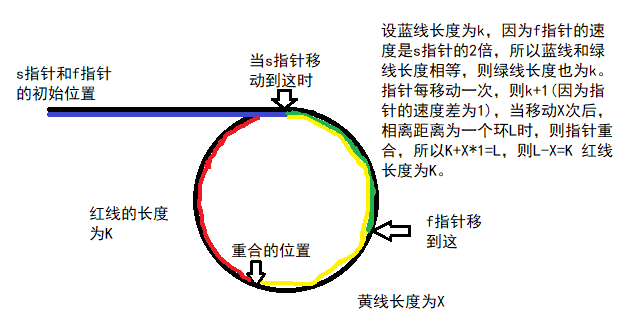
使用两个指针 s 和 f,s 指针每次移动一个结点,f 指针每次移动两个结点。如图:
- 执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
- 内存消耗:38.5 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了59.59%的用户
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
// 判断是否有环
do {
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return null;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
} while (slow != fast);
// 寻找环头
slow = head;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
5、两数相加(中等)
看题解后
方法一:模拟
自己写的过于复杂,题解答案:
- 执行用时:2 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
- 内存消耗:38.8 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了56.88%的用户
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode node = head;
// 是否需要进位
int carry = 0;
// 遍历链表
while (l1 != null || l2 != null) {
// 取出链表的值
int x = l1 == null ? 0 : l1.val;
int y = l2 == null ? 0 : l2.val;
// 求和
int sum = x + y + carry;
// 求进位
carry = sum / 10;
node.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
// 移动指针
node = node.next;
if (l1 != null) {
l1 = l1.next;
}
if (l2 != null) {
l2 = l2.next;
}
}
// 如果遍历完还需要进位,则创建新节点
if (carry == 1) {
node.next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return head.next;
}
}
6、反转链表(简单)
自己的想法
方法一:栈
- 执行用时:2 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
- 内存消耗:38.4 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了35.44%的用户
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
// 将链表中的所有节点入栈
while (head != null) {
stack.push(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
ListNode start = new ListNode();
ListNode node = start;
// 重新构造新的链表
while (!stack.empty()) {
node.next = new ListNode(stack.pop());
node = node.next;
}
return start.next;
}
}
看题解后
方法二:迭代
- 执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
- 内存消耗:38 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了88.40%的用户
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 当前节点
ListNode node = head;
// 记录前节点的
ListNode front = null;
while (node != null) {
// 取出下一个节点
ListNode next = node.next;
// 将当前节点指向前一个节点
node.next = front;
// 将当前节点记录成前节点
front = node;
// 更换当前节点
node = next;
}
return front;
}
}
方法三:递归
- 执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
- 内存消耗:38.5 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了17.57%的用户
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
// 返回节点头
ListNode node = reverseList(head.next);
// 构造反向链表,将当前节点的下一个节点指向自己
head.next.next = head;
// 将自己的指向清空
head.next = null;
return node;
}
}
标题:链表练习题——LeetCode
作者:Yi-Xing
地址:http://47.94.239.232/articles/2021/04/01/1617258251353.html
博客中若有不恰当的地方,请您一定要告诉我。前路崎岖,望我们可以互相帮助,并肩前行!